- Read more about:
- Robotic FUE
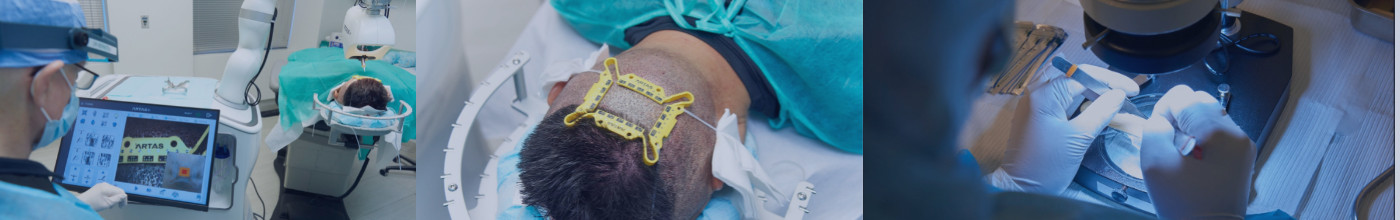
The ARTAS® Robotic System is the most advanced technology for surgical hair restoration. It aids the physician in performing Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplant procedures with accuracy and consistency that allows for maximum preservation of follicles.
Developed by the research engineers at Restoration Robotics, Inc., Mountain View, California, the ARTAS robot has been FDA-approved for robotic hair transplant surgery since the spring of 2011.
Dr. Bernstein is a clinical researcher and medical advisor to the company who has helped develop a number of the important new improvements to the system. Bernstein Medical was one of the first practices in the world to use robotic technology in hair transplantation and is now a beta-testing site for advances in the robotic system.
ARTAS Robot Components
The core components of the ARTAS robot are a robotic arm fitted with a sharp/blunt dual punch harvesting mechanism, an optical imaging system that scans the surface of the scalp and guides the robotic arm, a computer terminal networked with the robot’s central processor, a flat-screen TV display, a tensioner device that is applied to the patient’s scalp, and a chair with attached halo where the patient sits and rests his head.
The ARTAS robot also has the capability of recipient site making with ARTAS hair studio technology that allows the physician to design the hair transplant digitally.
How the ARTAS Robot Works
The latest version of the robot, called the ARTAS iX, improved upon the ARTAS 9x, that introduced a number of updates.
Tensioner
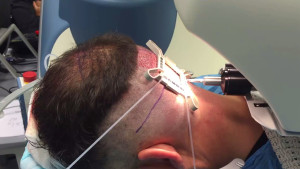
When the patient is anesthetized and prepared for graft extraction, the first step is for the physician to apply the “tensioner” to the patient’s scalp. The tensioner is a small plastic picture frame-like device that is applied to the scalp with traction to stretch the skin. It is then connected to a “halo” on the robotic chair to limit movement during the harvesting phase of the procedure.
The tensioner has a series of dots called fiducials on the perimeter of the frame which the robot’s optical system uses to orient the robotic arm and cutting tool. The space inside the frame is the active area in which the robot operates. The tensioner, as the name suggests, applies tension to the area to be harvested, which stabilizes the skin and limits skin movement during the procedure. The tension on the skin also decreases bleeding during the surgery. Interestingly, the robot can sense patient movement and will either adjust for it or temporarily halt the harvesting if the movement becomes excessive.
Parameters for Harvesting
At this time, the physician programs various parameters into the computer to guide the surgery. The most important of these include the needle diameter, inter-site spacing, and Follicular Unit Graft selection.
In the past, the doctor would also indicate the depth of the sharp and blunt punches, the angle at which the robot enters the scalp, and the speed of rotation of the blunt punch. However, these are now done automatically and it is just necessary for the physician to ensure that the robot is responding optimally.
Optical Guidance System
With the robotic arm in position and parameters set, the harvesting begins. The ARTAS robot’s optical system scans the surface of the scalp and selects a follicular unit for harvesting. The optical system magnifies the scalp allowing the robotic hair transplant to be performed with microscopic precision. Video from the optical system is projected in real-time on a large monitor and wall mounted TV, so that the surgeon and clinical staff can watch every movement the robot makes.
Dual Punch Mechanism
The mechanism used to isolate the follicular units from the surrounding tissue is a double-punch technology with an inner (sharp) punch and a rotating outer (dull) punch. During extraction, the inner punch scores the upper-most part of the skin and mild suction stabilizes the skin and allows the robot to follow the movements of the patient’s head. The rotating blunt edge of the outer punch then dissects the follicular unit from the surrounding tissue. This dual punch technology minimizes mechanical trauma and injury to the grafts and maximizes preservation of the follicles.
Once the graft has been isolated, the optical system scans the scalp and locates the next follicular unit for harvesting. The robotic arm then orients to the new target and the extraction process repeats.
Graft Harvesting
The robot harvests approximately 100 to 140 follicular unit grafts from each “grid” area defined by the tensioner. When harvesting in that area is complete the tensioner is moved to an adjacent area of the donor area. After each grid is complete, the grafts are removed and placed into a special chilled holding solution that contains a molecular energy source (ATP). This keeps the follicles healthy until they are placed in the balding area. The process continues until sufficient grafts have been harvested in the robotic hair transplant session.
Recipient Site Creation
The ARTAS robot creates recipient sites in the balding areas where the extracted follicular units are to be placed. In recipient site creation, the dual punch FUE harvesting tool is replaced by a blade that creates the recipient site incisions. The movement is guided by a program called the ARTAS hair studio. This translates the physician’s design into a 3-d model that guides the robotic surgery.
Dr. Bernstein has recognized that recipient sites made in advance of the harvesting, gives time for the healing process to begin and provides the ideal environment for transplanted grafts. As a result of this insight, he pioneered a technique of “pre-making recipient sites” to take advantage of this physiologic phenomenon. By making sites first, the recipient site is bathed in platelets and growth factors resulting in a more “fertile” environment for the grafts. This improves the grafts’ likelihood of optimal growth. At Bernstein Medical, we use the pre-making sites technique in all robotic hair transplant surgeries.
ARTAS Robot at Bernstein Medical
- Learn more about Robotic FUE:
- FAQ
- Answers
- Video
- Physician Consult
In the fall of 2011, Bernstein Medical became one of the first hair restoration facilities in the world to use the ARTAS system. We now perform all FUE procedures using the ARTAS robot. Dr. Bernstein has been working closely with Restoration Robotics for many years to improve the robot’s performance in FUE and to develop new applications.
Bernstein Medical is a beta-testing site for Restoration Robotics. It was in our facility in New York City where Dr. Bernstein débuted robotic recipient site creation, automated follicular unit graft selection and a number of other important updates.
The next phase of development involves the last phase of a hair transplant procedure, the placement of grafts into recipient sites. This process is currently in development and will likely take several years before it is available.
About Restoration Robotics
Restoration Robotics, Inc., is a privately-held medical device company based in Mountain View, CA and which is dedicated to developing and commercializing the first robotic device for hair transplantation – the ARTAS System. Restoration Robotics was founded by Dr. Frederick H. Moll, CEO of Hansen Medical, a publicly traded robotics company for invasive cardiac care instruments. Dr. Moll is a board member of Mako Surgical, an orthopedic robotics company. He is also the founder of Intuitive Surgical, the company that makes the Di Vinci Surgical System for the laparoscopic treatment of prostate cancer. Dr. Moll is considered a leader in the field of medical robotics.
Dr. Bernstein is a medical consultant to Restoration Robotics. He is involved in the research and development of the ARTAS System and has a financial interest in the company.